

"Isosceles" is made from the Greek roots "isos" (equal) and "skelos" (leg). A triangle that is not isosceles (having three unequal sides) is called scalene. The difference between these two definitions is that the modern version makes equilateral triangles (with three equal sides) a special case of isosceles triangles. Terminology, classification, and examples Įuclid defined an isosceles triangle as a triangle with exactly two equal sides, but modern treatments prefer to define isosceles triangles as having at least two equal sides. The two angles opposite the legs are equal and are always acute, so the classification of the triangle as acute, right, or obtuse depends only on the angle between its two legs. The other dimensions of the triangle, such as its height, area, and perimeter, can be calculated by simple formulas from the lengths of the legs and base.Įvery isosceles triangle has an axis of symmetry along the perpendicular bisector of its base. The two equal sides are called the legs and the third side is called the base of the triangle. Isosceles triangles have been used as decoration from even earlier times, and appear frequently in architecture and design, for instance in the pediments and gables of buildings. The mathematical study of isosceles triangles dates back to ancient Egyptian mathematics and Babylonian mathematics. Sometimes it is specified as having exactly two sides of equal length, and sometimes as having at least two sides of equal length, the latter version thus including the equilateral triangle as a special case.Įxamples of isosceles triangles include the isosceles right triangle, the golden triangle, and the faces of bipyramids and certain Catalan solids. In geometry, an isosceles triangle ( / aɪ ˈ s ɒ s ə l iː z/) is a triangle that has two sides of equal length. The book is especially a didactical material for the mathematical students and instructors.Isosceles triangle with vertical axis of symmetry One can navigate back and forth from the text of the problem to its solution using bookmarks. The solutions of the problems are at the end of each chapter. The degree of difficulties of the problems is from easy and medium to hard. After that, I have escaped in Turkey in September 1988 and lived in a political refugee camp in Istanbul and Ankara, and in March 1990 I immigrated to United States.
Properties of isosceles triangles deltamath plus#
This book is a translation from Romanian of "Probleme Compilate şi Rezolvate de Geometrie şi Trigonometrie" (University of Kishinev Press, Kishinev, 169 p., 1998), and includes problems of 2D and 3D Euclidean geometry plus trigonometry, compiled and solved from the Romanian Textbooks for 9th and 10th grade students, in the period 1981-1988, when I was a professor of mathematics at the "Petrache Poenaru" National College in Balcesti, Valcea (Romania), Lycée Sidi El Hassan Lyoussi in Sefrou (Morocco), then at the "Nicolae Balcescu" National College in Craiova and Dragotesti General School (Romania), but also I did intensive private tutoring for students preparing their university entrance examination. Acute angle: An angle whose measure is less then one right angle (i.e., less than 90 o), is called an acute angle. Right angle: An angle whose measure is 90 o is called a right angle. The amount of turning from one arm (OA) to other (OB) is called the measure of the angle (ÐAOB). In the figure above, the angle is represented as ∠AOB.
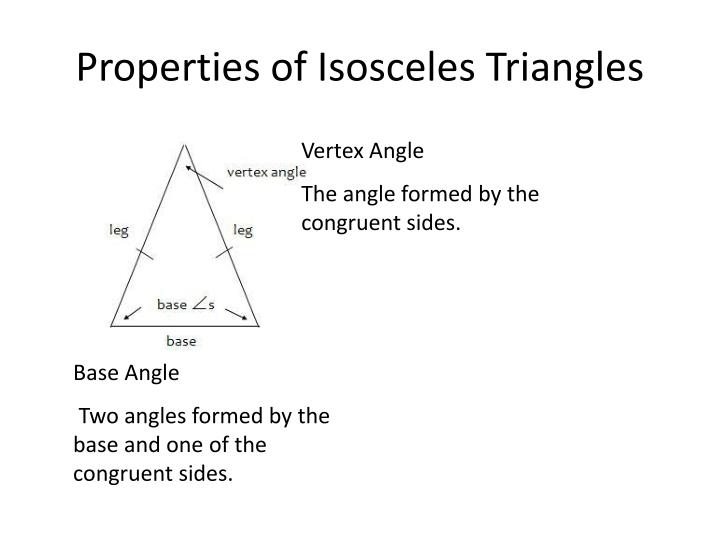
Angles: When two straight lines meet at a point they form an angle. Concurrent lines: If two or more lines intersect at the same point, then they are known as concurrent lines. The common point is known as the point of intersection. Intersecting lines: Two lines having a common point are called intersecting lines.

Ray: A line segment which can be extended in only one direction is called a ray. Line segment: The straight path joining two points A and B is called a line segment AB. It is a fine dot which has neither length nor breadth nor thickness but has position i.e., it has no magnitude. Fundamental concepts of Geometry: Point: It is an exact location.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
